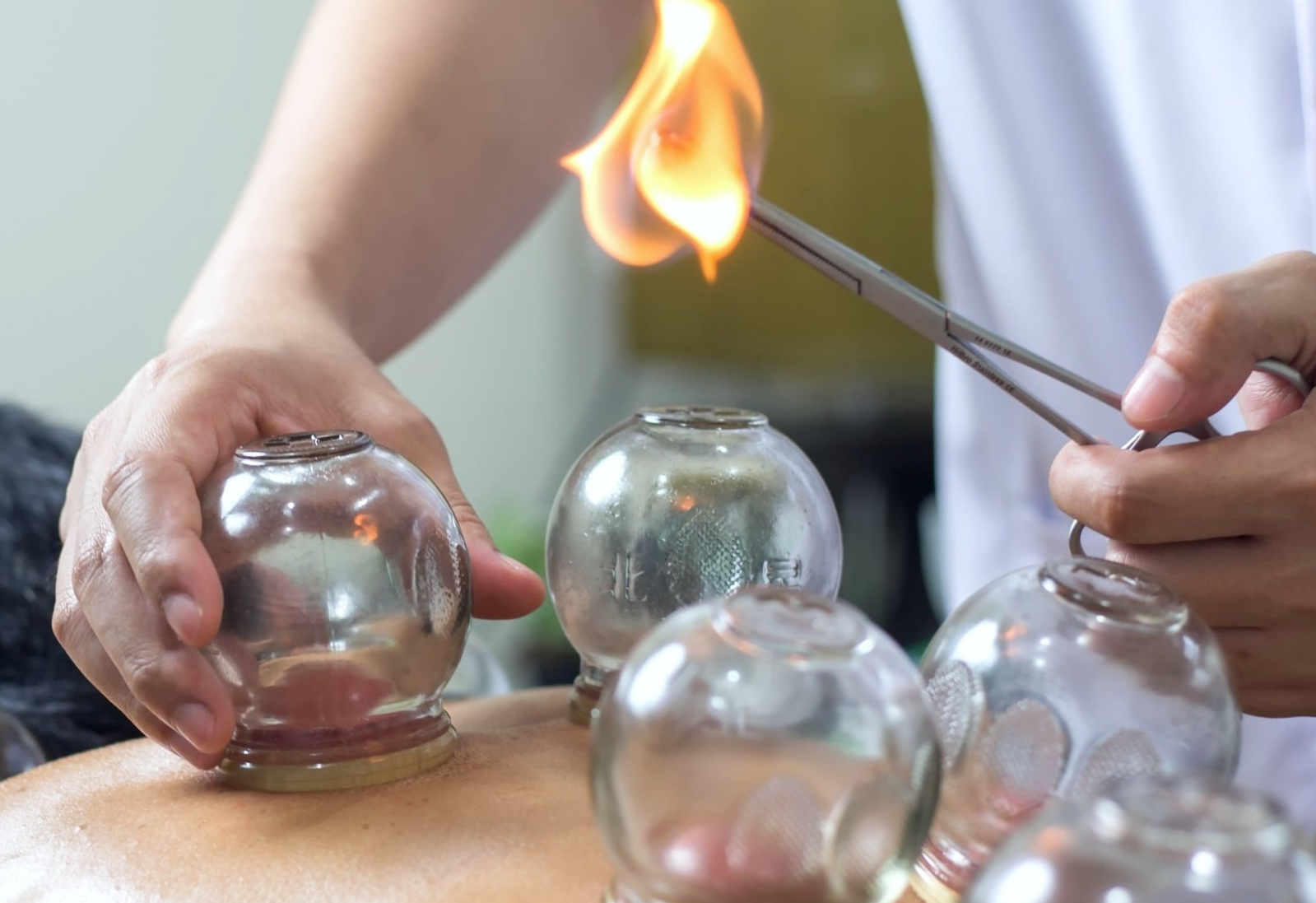
Dry Needling (DN) for Neck and Lower Back Pain
- by Joanna Blair
- •
- 10 May, 2025
- •
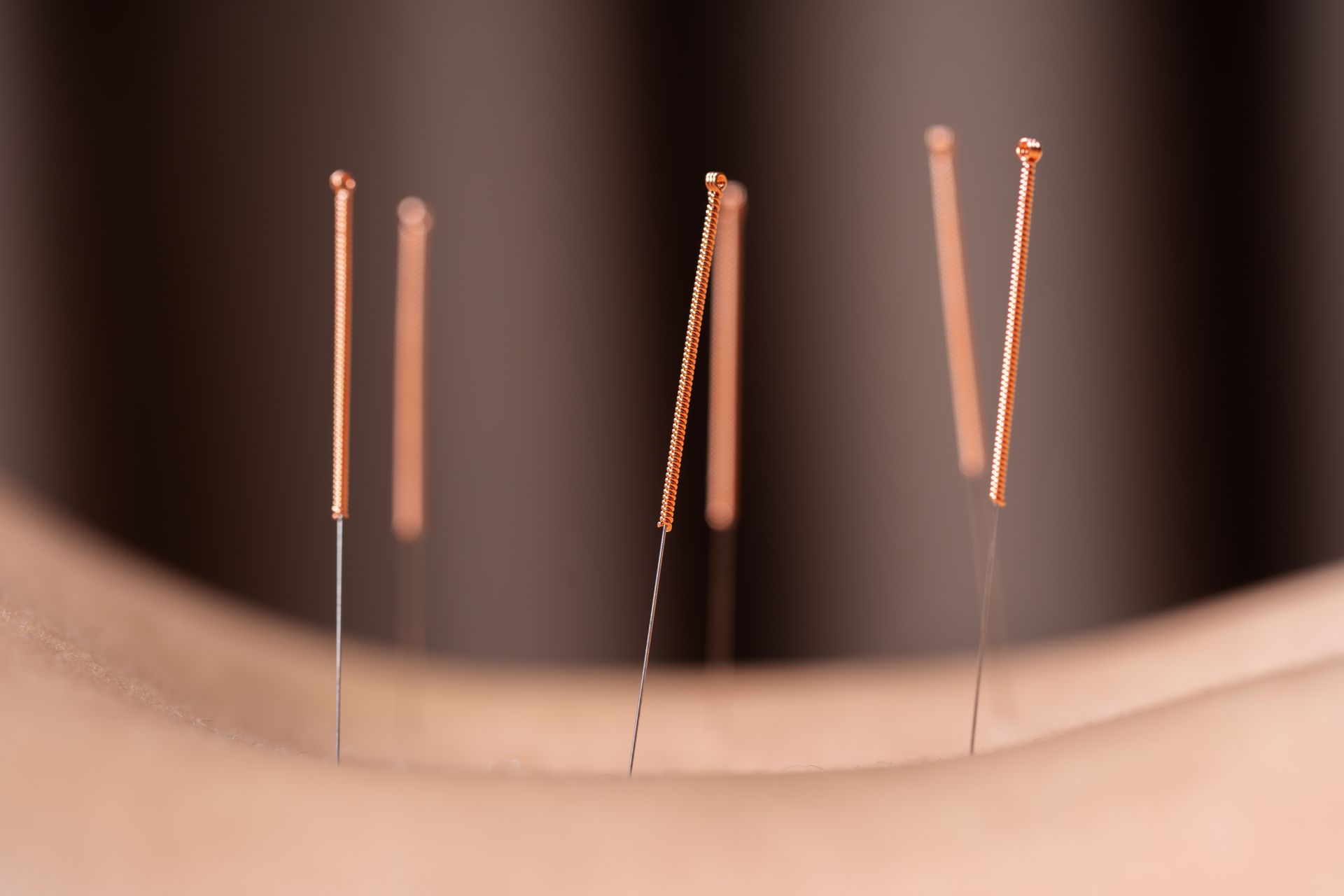
Dry needling (DN) is a standard form of treatment rapidly gaining in popularity amongst patients who seek newer options for the treatment of
mechanical neck and back pain-associated symptoms (1). Dry needling is also growing to become the most common intervention used in clinical practice for the management of trigger points (TPs). The treatment method involves a thin acupuncture needle to penetrate through the skin, subcutaneous tissues, and muscles (5). The puncture technique causes local muscle tremors which
relaxes the treated area and encourages the reduction of local tension and pain (5).
DN is developed along the theory of Myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) and differs to conventional acupuncture which is based on the theory of traditional Chinese medicine or placing acupunctures needles that relate to the meridians. DN involves a minimally invasive procedure consisting of inserting a high quality, sterile, disposable, solid flament needle into a myofascial trigger point (MTrP) without injecting or extracting any substances.
What Are Trigger Points?
A myofascial (muscle tissue) trigger point (MTP) is defined as a hyperirritable area within the skeletal muscle which has become hypersensitive. They are palpable nodules located in a taut band of muscle fibres and the area is painful when subjected to mechanical deformation through either compression, stretching, muscle contraction or other related stimuli (2). Trigger points produce pain locally in a referred pattern and often accompany chronic musculoskeletal disorders (2).
DN is developed along the theory of Myofascial trigger points (MTrPs) and differs to conventional acupuncture which is based on the theory of traditional Chinese medicine or placing acupunctures needles that relate to the meridians. DN involves a minimally invasive procedure consisting of inserting a high quality, sterile, disposable, solid flament needle into a myofascial trigger point (MTrP) without injecting or extracting any substances.
What Are Trigger Points?
A myofascial (muscle tissue) trigger point (MTP) is defined as a hyperirritable area within the skeletal muscle which has become hypersensitive. They are palpable nodules located in a taut band of muscle fibres and the area is painful when subjected to mechanical deformation through either compression, stretching, muscle contraction or other related stimuli (2). Trigger points produce pain locally in a referred pattern and often accompany chronic musculoskeletal disorders (2).
DN & Chronic Neck Pain
Herna ́ndez-Secoru ́n et al., (2023) supported the conclusion that dry needling (DN) can improve pain and functional capacity in patients with chronic neck pain at short and mid-term intervals. According to the study's findings, DN showed to be more effective when compared with other therapies including stretching, manual therpy, myofascial release and TENS with ultrasound in both women and men (4). When the analysis was carried out by age, patients over 40 years old benefitted more than those below 40 years of age (4).
DN & Lower Back Pain
Hu et al.,
(2018) found dry needling to be more effective than acupuncture or sham needling (a procedure that mimics needling techniques but does not involve penetration of the skin). They found evidence to reveal that DN is more effective for alleviating pain
intensity and functional disability at postintervention in lower back pain (3).
Another study by Rajfur et al., (2022)assessed the effectiveness of dry needling for reducing pain intensity and improving functional efficiency in patients with chronic lower back pain due to the L5-S1 discopathy. They found that dry needling effectively reduced pain and improved range of motion of local joints in patients with chronic lower back pain (5).
Another study by Rajfur et al., (2022)assessed the effectiveness of dry needling for reducing pain intensity and improving functional efficiency in patients with chronic lower back pain due to the L5-S1 discopathy. They found that dry needling effectively reduced pain and improved range of motion of local joints in patients with chronic lower back pain (5).
Demonstration
References
1. Aleid, A. M., Aljabr, A. A., Aldanyowi, S. N., AlAidarous, H. A., Aleid, Z. M., Alharthi, A. S., Alsubaie, M. N., AlOraini, L. I., Almoslem, A. R., (2025) Mutair, A. A. (2025) Dry Needling for Mechanical Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Surgical Neurology International (SNI), 16; 44: 1-8.
2. Alvarez, D. J., Rockwell, P. G., (2002) Trigger Points: Diagnosis and Management, American Family Physician, 65; 4: 653-660.
3. Hu, H. T., Gao, H., Ma, R-J., Zhao, X-F., Tian, H-F. Li, L. (2018) Is dry needling effective for low back pain? A systematic review and PRISMA-compliant meta-analysisMedicine, 97; 26: 1-10.
4. Hernandez-Secorun, M., Abenia-Benedı ́, H., Borrella-Andre ́s, S., Marque ́s-Garc ́ıa, I., Lucha-Lo ́pez, M. O., Herrero, P., Iguacel, I., Trica ́s-Moreno, J. M., Hidalgo-Garcı ́a, C. (2023) Effectiveness of Dry Needling in Improving Pain and Function in Comparison with Other Techniques in Patients with Chronic Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Pain Research Management, 1-14.
5. Rajfur, R., Rajfur, R., Kosowski, T., Walewicz, K., Dymarek, R., Ptaszkowski, K., Taradaj, J. (2022) The effectiveness of dry needling in patients with chronic low back pain: a prospective, randomized, single‑blinded study, Scientific Reports, Nature Portfolio, 12; 15803: 1-11.
2. Alvarez, D. J., Rockwell, P. G., (2002) Trigger Points: Diagnosis and Management, American Family Physician, 65; 4: 653-660.
3. Hu, H. T., Gao, H., Ma, R-J., Zhao, X-F., Tian, H-F. Li, L. (2018) Is dry needling effective for low back pain? A systematic review and PRISMA-compliant meta-analysisMedicine, 97; 26: 1-10.
4. Hernandez-Secorun, M., Abenia-Benedı ́, H., Borrella-Andre ́s, S., Marque ́s-Garc ́ıa, I., Lucha-Lo ́pez, M. O., Herrero, P., Iguacel, I., Trica ́s-Moreno, J. M., Hidalgo-Garcı ́a, C. (2023) Effectiveness of Dry Needling in Improving Pain and Function in Comparison with Other Techniques in Patients with Chronic Neck Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Pain Research Management, 1-14.
5. Rajfur, R., Rajfur, R., Kosowski, T., Walewicz, K., Dymarek, R., Ptaszkowski, K., Taradaj, J. (2022) The effectiveness of dry needling in patients with chronic low back pain: a prospective, randomized, single‑blinded study, Scientific Reports, Nature Portfolio, 12; 15803: 1-11.